a. Identify time intervals where TCP slow-start is operating.
TCP Congestion Control Exercises (Solutions)
Please try these yourself first before looking up solutions.
In the following, cwind stands for Congestion Window and ssthreshold stands for Slow Start Threshold.
1. The difference between “Flow Control” and “Congestion Control” as applied to TCP transmission is: Flow control is the receiver controlling how much the sender is injecting into the network, whereas Congestion Control is the sender sensing congestion on the network by timing ACKs and controlling its sending rate.
When the retransmission timer expires at the sender, the value of ssthreshold is set to ½ the current cwind value.
cwind parameter is taken
from : (e) – it is not in TCP header, but
determined solely by sending TCP.
a) sender tcp header
b)
receiver tcp header
c) sender tcp's window parameter
e)
receiver tcp's window
e) None of the above
When TCP is in slow start, receipt of 2 ACKs before timeout results in cwind being increased by 2 MSS bytes
a) ssthreshold parameter determines when slow start ends and congestion-avoidance takes over.
In congestion avoidance phase, TCP's send rate increases linearly.
Why does TCP Reno get rid of slow start phase when a triple duplicate ACK is received? The receipt of triple duplicate ACKs indicates that some segments are getting through, and so congestion may be less severe. Thus instead of wasting bandwidth, TCP tries a more aggressive strategy, by starting cwind at the current ssthreshold value rather than at 1 MSS. This is ½ the cwind value when the packet was dropped.
What is “fast re-transmit”? In TCP Reno, when three duplicate ACKs are received, TCP retransmits the packet presumed lost without waiting for timeout. This is called fast-retransmit.
What is “fast recovery”? In TCP Reno, when TCP does fast re-transmit (see above question), instead of beginning a slow-start phase with cwind set to 1, it goes directly to congestion-avoidance phase, with cwind set to ½ its value when packet loss occurred. This is called fast recovery. Fast re-transmit and fast-recovery are usually implemented together.
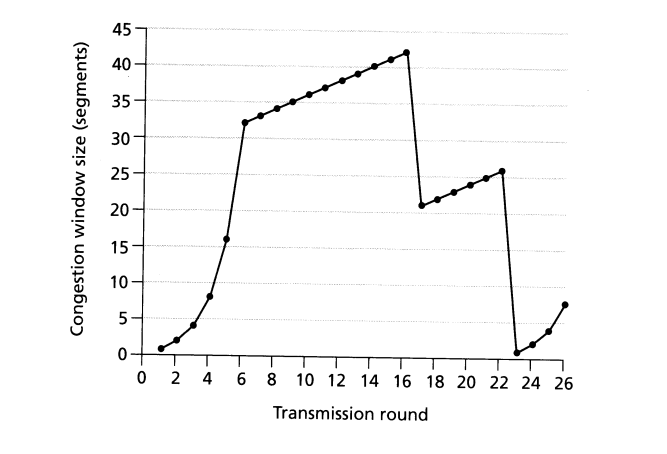
The picture below shows the behavior of a TCP Reno.

a.
Identify time intervals where TCP slow-start is operating.
TCP slowstart is operating in the intervals [1,6] and [23,26]
b. Identify time intervals where TCP congestion-avoidance is operating
TCP congestion advoidance is operating in the intervals [6,16] and [17,22]
c. After the 16th transmission round, is segment loss detected by a triple duplicate ACK or by a timeout event?
After the 16th transmission round, packet loss is recognized by a triple duplicate ACK. If there was a timeout, the congestion window size would have dropped to 1.
d. After the 22nd transmission round, is segment loss detected by a triple duplicate ACK or by a timeout event?
After the 22nd transmission round, segment loss is detected due to timeout, and hence the congestion window size is set to 1 (remember that this means that TCP can send up to 1 MSS ).
e. What is the ssthreshold value at the first transmission round?
The threshold is initially 32, since it is at this window size that slowtart stops and congestion avoidance begins.
f. What is the ssthreshold value at the 18th transmission round?
The threshold is set to half the value of the congestion window when packet loss is detected. When loss is detected during transmission round 16, the congestion windows size is 42. Hence the threshold is 21 during the 18th transmission round.
g. What is the ssthreshold value at the 24th transmission round?
The threshold is set to half the value of the congestion window when packet loss is detected. When loss is detected during transmission round 22, the congestion windows size is 26. Hence the threshold is 13 during the 24th transmission round.
h. What will be the values of cwind and ssthreshold if packet loss is detected after the 26th round by receipt of triple duplicate ACKs?
The congestion window and threshold will be set to half the current value of the congestion window (8) when the loss occurred. Thus the new values of the threshold and window will be 4.